Geothermal power harnesses the Earth’s internal heat to generate electricity and provide direct heating solutions. As the world seeks sustainable energy sources, geothermal energy stands out as a reliable and eco-friendly alternative. This article explores how geothermal energy works, its benefits, challenges, and its potential role in a sustainable future.
What is Geothermal Energy?
Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source derived from the Earth’s heat. This heat originates from the planet’s formation and the radioactive decay of minerals deep within the Earth. The Earth’s crust acts as an insulating layer, allowing this heat to accumulate and be utilized effectively.
Sources of Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy can be sourced from various geological formations:
- Volcanic Activity: Regions near tectonic plate boundaries often experience volcanic activity, providing a rich source of geothermal energy. Famous examples include Iceland, where geothermal power significantly contributes to the national grid.
- Hot Springs: Natural hot springs, found in various parts of the world, can be tapped for geothermal energy. These springs are often used for heating buildings or in spa resorts.
- Deep-Earth Heat: In some cases, the heat is extracted from deep underground, where temperatures can reach several hundred degrees Celsius. This heat can be harnessed for electricity generation in geothermal power plants.
How Geothermal Power Works
Geothermal Power Plants
Geothermal power plants convert heat from the Earth into electricity. There are three main types of geothermal plants:
- Dry Steam Plants: These plants use steam directly from geothermal reservoirs to turn turbines and generate electricity. This is the oldest type of geothermal plant and is primarily found in places with high-temperature resources.
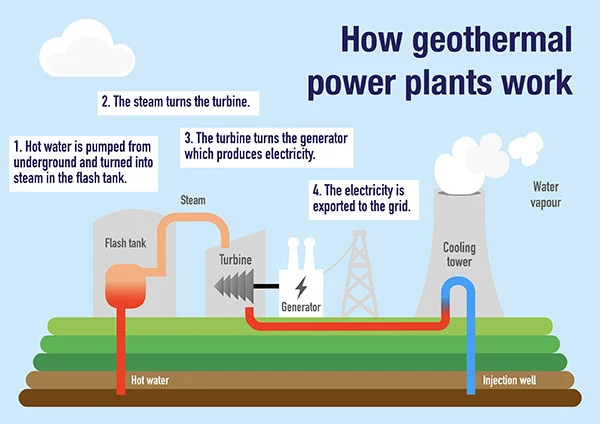
- Flash Steam Plants: In flash steam plants, high-pressure hot water from geothermal reservoirs is brought to the surface. As the pressure decreases, some of the water flashes into steam, which then drives the turbines. The remaining water can be reinjected into the reservoir.
- Binary Cycle Plants: These plants use a secondary fluid with a lower boiling point than water. The geothermal water heats this fluid, which vaporizes and drives the turbines. This method is more versatile and can be used in lower-temperature geothermal resources.
Process of Electricity Generation
The electricity generation process in a geothermal plant involves several key steps:
- Heat Extraction: Hot water or steam is extracted from underground reservoirs using wells drilled into the Earth.
- Turbine Activation: The extracted steam or heated fluid is used to turn turbines connected to generators.
- Electricity Generation: As the turbines spin, they generate electricity, which is then transmitted to the power grid.
- Reinjection: After the heat has been extracted, the cooled water is usually reinjected back into the geothermal reservoir to maintain pressure and sustainability.
Benefits of Geothermal Energy
Renewable and Sustainable
Geothermal energy is a renewable resource, meaning it can be continuously replenished. Unlike fossil fuels, which deplete over time, geothermal energy relies on the Earth’s internal heat, which is vast and virtually inexhaustible.
Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the most significant advantages of geothermal energy is its low environmental impact. Geothermal plants produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel plants. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), geothermal can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 97% compared to coal-fired power plants.
Reliable Energy Source
Geothermal energy provides a stable and reliable source of power. Unlike solar and wind energy, which are intermittent and dependent on weather conditions, geothermal plants can operate continuously, providing baseload energy. This reliability makes geothermal energy a valuable addition to the energy mix, ensuring a consistent power supply.
Economic Benefits
Investing in geothermal energy can lead to job creation and economic growth. Geothermal plants require skilled labor for construction, operation, and maintenance, creating numerous jobs in local communities. Furthermore, geothermal energy can contribute to energy independence by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Low Operating Costs
Once a geothermal power plant is established, the operating costs are relatively low. The cost of extracting geothermal energy is stable and less susceptible to market fluctuations compared to fossil fuels, leading to more predictable energy prices for consumers.
Challenges Facing Geothermal Energy
Location Limitations
One of the primary challenges of geothermal energy is its geographical limitations. Geothermal resources are not evenly distributed around the world. Regions with the most significant geothermal potential, such as Iceland and the Pacific Ring of Fire, are often located near tectonic plate boundaries. This means that not all areas can access geothermal energy.
High Initial Costs
The initial investment for geothermal power plants can be substantial. The costs associated with drilling wells, building infrastructure, and conducting exploratory studies can be significant barriers to entry. While operational costs may be low, securing funding for the upfront expenses can be challenging for developers.
Resource Depletion Risks
While geothermal energy is renewable, there is a risk of resource depletion if the geothermal reservoirs are not managed sustainably. Over-extraction of heat can lead to a decrease in reservoir pressure and temperature, impacting the plant’s efficiency. Proper management and reinjection strategies are crucial to maintain the sustainability of geothermal resources.
Future of Geothermal Energy
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are paving the way for the future of geothermal energy. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) represent a significant breakthrough. EGS involves injecting water into hot, dry rock formations, creating artificial reservoirs that can be used to generate electricity. This technology expands the potential for geothermal energy to areas previously considered unsuitable for geothermal development.
Global Growth Trends
The global geothermal market is on the rise, with countries like the United States, Indonesia, and the Philippines leading in geothermal energy production. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), global installed geothermal capacity reached over 14,000 megawatts in 2020, and this number is expected to grow as more countries recognize the benefits of geothermal energy.
Potential in Urban Areas
Geothermal heating systems are becoming increasingly popular in urban areas, where they can provide efficient heating for buildings. Ground-source heat pumps, for example, use the Earth’s stable temperature to provide heating and cooling, significantly reducing energy consumption in residential and commercial buildings.
How to Get Involved in Geothermal Energy
Investing in Geothermal Projects
Investors looking to fund renewable energy initiatives should consider geothermal projects. Many countries offer incentives and programs to encourage investment in geothermal energy, making it an attractive option for those interested in sustainable energy solutions.
Government Incentives
Governments worldwide are recognizing the importance of renewable energy and providing support for geothermal initiatives. Incentives may include grants, tax credits, and low-interest loans to facilitate the development of geothermal power plants and heating systems.
Community Initiatives
Community involvement is crucial for the growth of geothermal energy. Local organizations and governments can collaborate to promote geothermal heating systems for residential and commercial use. Raising awareness about the benefits of geothermal energy can lead to greater adoption and investment in sustainable energy solutions.
Conclusion
Geothermal energy presents a promising solution to the global energy crisis, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional energy sources. As technology advances and awareness increases, the potential of geothermal power will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping our energy future. By investing in geothermal projects and supporting community initiatives, we can unlock the Earth’s energy and pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable tomorrow.