Protect Your Data with macOS: The Ultimate Guide to Malware Defense
Protect Your Data with macOS. In today’s connected world, protecting your data from malware is more essential than ever. Malware can steal sensitive information, disrupt your system, and even demand ransom to return control of your data. Thankfully, macOS includes robust, layered security features to keep your Mac and personal data safe. This guide explores the tools macOS offers to defend against malware and how you can further secure your device.
What is Malware and Why is It a Threat?
Malware, short for “malicious software,” is designed to damage or disrupt your system, steal information, or compromise device functionality. It comes in various forms, such as viruses, Trojan horses, ransomware, and spyware. With an increasing number of online activities and cloud-based services, malware attacks are growing rapidly. macOS offers strong defenses, but it’s still essential to understand how to enhance your system’s protection.
Protect Your Data with macOS
macOS Security Features That Shield Against Malware
macOS utilizes several in-built security features to protect your data. These mechanisms work together to restrict unauthorized software and actions on your Mac.
Protect Your Data with macOS
1. Gatekeeper: Your First Line of Defense
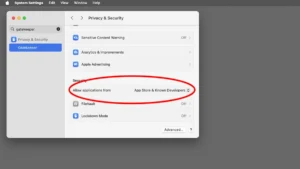
Introduced to prevent malware from running, Gatekeeper only allows software from recognized developers with Apple’s Developer ID to run on your Mac. If you attempt to open an app from an unknown developer, Gatekeeper will warn you, offering an extra layer of protection.
To customize Gatekeeper:
- Go to System Settings > Privacy & Security > Allow Applications.
- Choose to allow apps from the App Store only or App Store & Known Developers.
This feature ensures that any app without verified credentials cannot automatically launch on your Mac. Only trusted software gets through, minimizing the risk of malware infections.
2. System Integrity Protection (SIP)
System Integrity Protection (SIP) is a built-in feature that safeguards essential system files and processes from unauthorized modifications. SIP prevents malware from altering system files or running malicious scripts that might jeopardize system stability. Apple recommends leaving SIP enabled to avoid weakening macOS’s overall security.
Protect Your Data with macOS
To check the SIP status:
- Open Terminal.
- Type
csrutil statusand press Enter.
SIP enhances macOS’s defense by ensuring system processes remain uncompromised, shielding sensitive files from tampering.
3. Developer ID and App Notarization
Every app on macOS is assigned a Developer ID, which serves as a digital signature, allowing Apple to verify its authenticity. Apple also performs an additional layer of verification, known as app notarization, which checks apps for malicious code before they are downloaded.
Protect Your Data with macOS
If you download an app that lacks a Developer ID or notarization, macOS will notify you before allowing it to run, giving you an extra opportunity to confirm the app’s legitimacy. This extra check helps prevent unauthorized or compromised software from executing on your Mac.
4. Hardened Runtime Protection
Apple’s Hardened Runtime protection works in conjunction with SIP to block unauthorized code injection or runtime modifications. This makes it harder for attackers to inject malicious code that could hijack your applications or steal data.
Using Hardened Runtime settings, developers specify which permissions their apps need, limiting the potential for malicious exploits.
Additional Tools and Best Practices to Strengthen macOS Security
Beyond built-in macOS features, you can further secure your system by adopting specific settings and behaviors:
1. Limiting Administrative Privileges
macOS assigns elevated privileges to users with administrative rights, allowing them to install software, manage security settings, and control system-wide functions. To prevent malware from exploiting administrative privileges:
- Only grant admin access when absolutely necessary.
- Limit the number of users with admin permissions.
- Use an account with standard permissions for everyday use.
Protect Your Data with macOS
2. Disable Root User Access
The root user, with unlimited control over the system, is disabled by default on macOS to prevent unauthorized access. This security measure makes it challenging for malware to modify core settings or install itself at the system level.
3. Use Helper Tools and Temporary Privilege Escalation
Helper tools allow apps to run with minimal privileges, requesting elevated access only for critical tasks. By containing privileged operations in a helper tool, the primary app remains secure, reducing the risk of compromise by limiting permissions to the smallest amount of time necessary.
Protect Your Data with macOS
4. Network Security Practices
Network attacks are a common malware entry point. To secure your Mac from these types of threats:
- Enable the highest security settings in your web browser.
- Avoid downloading content from untrusted websites.
- Disable Remote Login and Remote Management unless explicitly required.
You can manage these settings in System Settings > Sharing. By controlling network access, you protect your system from remote attacks and unauthorized logins.
Protect Your Data with macOS
macOS Security Frameworks and Daemons
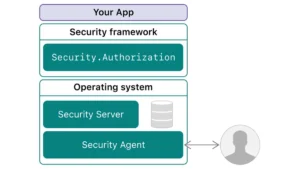
macOS operates on a UNIX-based architecture, utilizing security frameworks and daemons to monitor processes and protect your data. Key frameworks include:
- launchd: Manages launching and terminating apps, including background tasks.
- Authorization Services.framework: Handles admin privilege requests.
- Security.framework: Secures user identity and data.
- Endpoint Security.framework: Enables developers to write security-enhancing system extensions.
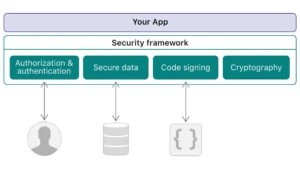
macOS also features Cryptographic Services and Keychain Services, which securely store passwords, cryptographic keys, and certificates. These services keep sensitive data encrypted and accessible only by authenticated users.
Protect Your Data with macOS
Defending Against Different Types of Malware
Malware comes in various forms, and each type requires a unique approach for defense. Here’s a look at some of the most common malware threats and how macOS helps defend against them:
- Viruses: By enforcing privileges and limiting root access, macOS minimizes the ability of viruses to spread system-wide. Periodic scans can help you detect viruses in their early stages.
- Trojan Horses: Gatekeeper alerts you to unauthorized applications, helping prevent Trojan horses from infiltrating your system.
- Ransomware: SIP and Developer ID offer robust protection, reducing the risk of ransomware gaining control of your data.
For additional protection, consider running trusted antivirus or malware detection software. Although macOS is inherently secure, periodic scans can identify hidden threats.
Protect Your Data with macOS
Practical Tips to Keep Your Mac Secure
To maintain optimal security on your Mac, follow these tips:
- Install apps only from the App Store or verified sources.
- Limit the number of installed apps to reduce potential vulnerabilities.
- Disable Guest access and avoid sharing admin privileges.
- Regularly scan your system for malware and check for software updates.
- Adjust network security settings in your browser and use a secure Wi-Fi password.
Protect Your Data with macOS
The Bottom Line
macOS has a comprehensive security model designed to protect your data from malware. With features like Gatekeeper, System Integrity Protection, and Hardened Runtime, it provides an impressive defense against threats. By adopting secure usage practices and limiting app installations to trusted sources, you can keep your Mac safe and enjoy worry-free computing.
Protecting your Mac doesn’t require complex software or constant monitoring—macOS handles much of it automatically. Stay vigilant, follow best practices, and let macOS’s robust security tools do the rest.
Protect Your Data with macOS
Protect Your Data with macOS
Protect Your Data with macOS
